上一篇文章中描述了LVS的配置,但LVS有一个缺陷:不探测Real Server的状态,就算是Real Server宕机,LVS也会把请求转发过去。
使用Keepalived可以弥补LVS的缺陷,还可以实现LVS Director的冗余备份,keepalived会根据主机的健康状况让VIP在LVS Director之间漂移。同时Keepalived还可以替代ipvsadm工具,在keepalived配置文件中直接完成LVS的配置。
1. 配置网络结构:
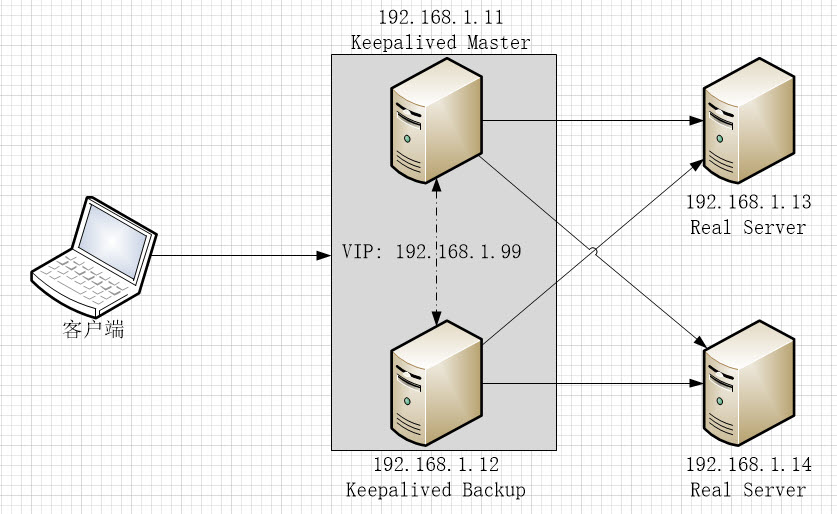
- 192.168.1.11和192.168.1.12是互为备份的LVS Director, 192.168.1.11默认为MASTER, 192.168.1.12为BACKUP
- 192.168.1.99是LVS Director的虚拟IP,当192.168.1.11正常工作时,它会通过VRRPv2协议向广播网段发送ARP数据包,声明192.168.1.99为其所有,当192.168.1.11宕机时,192.168.1.12会立即接管该工作,声明192.168.1.99的所有权并响应用户请求
- 192.168.1.13和192.168.1.14是 Real Server, 上面有监听在80端的Web 服务
2. Keepalived主机安装配置
1. 在192.168.1.11和192.168.1.12上安装keepalived, 安装完成后修改配置文件/etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf。
# yum install keepalived -y
# vi /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
详细配置参数说明请参见官方文档:http://www.keepalived.org/doc/configuration_synopsis.html
2. 配置MASTER节点(192.168.1.11),配置文件内容如下。关键配置内容添加了注释:
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id LVS_11 #节点ID,每个节点的值唯一
vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr
vrrp_strict #严格遵守VRRP,三种情况将会阻止keepalived (1.无VIPs, 2.unicast peers,3.IPv6 addresses in VRRP version 2)
vrrp_garp_interval 0
vrrp_gna_interval 0
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 { #定义一个实例(高可用集群)
state MASTER #节点在Keepalived中定义为MASTER
interface enp0s3 #指定节点发送ARP数据报时使用的网关设备
virtual_router_id 51 #Virtual Router ID, 数字格式,集群中的所有节点值要相同,
priority 101 #节点优先级,MASTER节点要比其它节点的值大
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS #节点间的认证方式,支持PASS, HEAD
auth_pass keepsync #auth_type为PASS时的主证密码,超过8位则keepalived只取前8位
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.1.99 #配置虚拟IP
}
}
--------------------------------------分割线,如果只配置Keepalived主备集群,上面的配置就可以了,下面的配置用于配置LVS--------------------------------
virtual_server 192.168.1.99 80 { #配置LVS集群服务地址及端口
delay_loop 6
lb_algo lc #LVS请求分配算法,当前为LC,详见LVS文档
lb_kind DR #LVS工作模式为DR
persistence_timeout 50
protocol TCP #LVS服务协议为TCP
real_server 192.168.1.13 80 { #Real Server 1 地址及端口
weight 1 #Real Server 1权重
TCP_CHECK { #Real Server健康诊断方式为TCP_CHECK, 支持的方式有TCP_CHECK, HTTP_GET, SSL_GET, MISC_CHECK
connect_timeout 3 #诊断间隔为3秒
connect_port 80 #诊断连接端口为80
}
}
real_server 192.168.1.14 80 { #Real Server 1 配置
weight 1
TCP_CHECK {
connect_timeout 3
connect_port 80
}
}
}
3. 配置BACKUP节点(192.168.1.12):
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id LVS_12 #每个节点唯一,与其它节点不周
vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr
vrrp_strict
vrrp_garp_interval 0
vrrp_gna_interval 0
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP #指定为BACKUP模式
interface enp0s3
virtual_router_id 51 #与其它节点相同
priority 100 #优先级比MASTER低
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass keepsync
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.1.99
}
}
virtual_server 192.168.1.99 80 {
delay_loop 6
lb_algo lc
lb_kind DR
persistence_timeout 50
protocol TCP
real_server 192.168.1.13 80 {
weight 1
TCP_CHECK {
connect_timeout 3
connect_port 80
nb_get_retry 3
delay_before_retry 3
}
}
real_server 192.168.1.14 80 {
weight 1
TCP_CHECK {
connect_timeout 3
connect_port 80
}
}
}
Keepalived会按TCP_CHECK中配置的connect_timeout时间间隔尝试连接real server的connect_port指定的端口,如果指定server的指定端口不可达,该real server会被从LVS集群中移除,待该server恢复后又会被自动加入到集群。
关于Health Check的详细信息请参见:http://www.keepalived.org/doc/software_design.html#healthcheck-framework
4. 在MASTER和BACKUP节点上启动并启用keepalived服务:
# systemctl start keepalived
# systemctl enable keepalived
如果Keepalived MASTER节点上安装了ipvsadm管理工具,可以看到LVS配置已经生成:
[root@centos01 ~]# ipvsadm -Ln
IP Virtual Server version 1.2.1 (size=4096)
Prot LocalAddress:Port Scheduler Flags
-> RemoteAddress:Port Forward Weight ActiveConn InActConn
TCP 192.168.1.99:80 lc persistent 50
-> 192.168.1.13:80 Route 1 0 0
-> 192.168.1.14:80 Route 1 0 6
5. 在MASTER和BACKUP节点上启用ip_forward:
# cat << EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/zz-keepalived.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOF
# sysctl --system
/etc/sysctl.d目录下, 文件名排序越靠后,优先级越高, 所以以zz-..作为文件名前缀
3. Real Server配置
LVS工作在DR模式时,Real Server需要直接与客户端通讯,因此需要把VIP配置在Real Server上,并且不允许以该VIP的名义向广播网段发送ARP数据包,做如下配置:
# ifconfig enp0s3:0 192.168.1.99 netmask 255.255.255.255 up
# echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/enp0s3/arp_ignore
# echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_ignore
# echo "2" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/enp0s3/arp_announce
# echo "2" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_announce
至此,相关配置全部完成。如果Real Server上的Web服务工作正常,通过浏览器访问VIP就可以正常打开Real Server上的Web服务了,如果MASTER节点停止服务,BACKUP节点会立即接管,待MASTER恢复后则重新接管服务。如果某一个Real Server停止,则该Real Server则会被从LVS集群中移动,恢复后又会被自动加入到LVS集群中。
如果keepalived.conf文件中不配置virtual_server, keepalived就单纯提供双机热备服务,让VIP在主备机之间漂移。
为保证Keepalived 节点和Real Server之间通讯正常,最好停掉各个Server上的和防火墙(firewalld)服务,或者每改动一次配置都需要重新执行一下iptables -F。
